Use cases
Get more out of it! LiDAR Scanner – (3) [How to collect data as “usable” as possible with LiDAR scanner applications – Part 2]

Continuing from LiDAR scanner – (2) [How to collect data as “usable” as possible with LiDAR scanner applications – Part 1], this article explains the results of our investigation on what can be done to collect the most usable data using 3D measurement applications for the iPhone/iPad LiDAR scanner.
This article explains how to collect more useful data using our original LiDAR scanner application, “Sakura3D SCAN,” in addition to the items common to various 3D measurement applications.
Survey subjects
- Properties of the target object (color, reflection, size)
- Measurement method
- Making better use of the Sakura3D SCAN features
Survey 1: Properties of the target object (color, reflection, size)
This study examined whether the results would vary depending on the color of the target object, the material reflecting the light, and the size of the target object.
Color
Below are the images that were captured by the survey.
As you can see from the actual photo, it includes different colors: white, black, brown for the floor, and more.
Looking at the captured image of the measured point cloud, there is no difference in the resulting image due to color.


We expected to see a difference between white and black, but there is little difference.
Although not all colors have been tested, we did not expect a problem with any color.
Reflection
Below are the images that were captured by the survey.
A pipe made of a light-reflecting material was scanned.
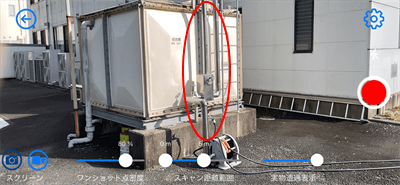

It was not impossible to scan such an object, but the resulting image contained a large amount of noise around the object.
To solve the noise problem, the light-reflecting object was scanned when it was not exposed to sunlight (in the shade). As a result, the noise was reduced. Please see the comparison images below.
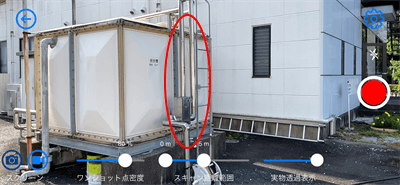

For objects with light-reflecting material, it is recommended to scan them when not exposed to sunlight.
Size
Below are the images that were captured by the survey.


This article shares some aspects with Part 1, “Survey 3: Density of the point cloud to be obtained.” If a target object is scanned with a 100% density, an area of up to 7 × 5 m can be captured in a single shot.
For an area larger than 7 × 5 m, it is necessary to reduce the density or take more than one shot and then align them in post-processing. However, there will be more or fewer errors during the alignment process, reducing the accuracy.
If you are considering using the iPhone/iPad LiDAR scanner in the future, it is recommended that you take images of an area up to 7 × 5 m at 100% density (based on the reference in Sakura3D). If the area to be scanned is larger than 7 × 5 m, we recommend reducing the density or taking multiple shots.
Survey 2: Scanning method
Here are some things we noticed through repeated measurements rather than through the survey.
When scanning a target, you will probably hold your iPhone/iPad over the target and take pictures while moving your iPhone/iPad. It is important that you do not move your iPhone/iPad back and forth many times.
The more you go back and forth, the less accurate the result will be, causing misalignment due to excessive point cloud overlap.
The images below compare the point clouds obtained in one round trip and four round trips.
The image obtained by four round trips shows a blur in the outline of the object and a distortion of the geometry itself.


Survey 3: Making better use of the Sakura3D SCAN features
Here, we explain how to use the Sakura3D SCAN features to obtain the most accurate data possible. The following three features are explained:
- Stop function
- Photographic-style measurement
- AI auto-recognition feature
Stop function
In addition to the Sakura3D SCAN, some LiDAR scanner applications have a feature to pause the measurement in progress. If such a feature is available, it is worth using it.
This feature is useful for accurate measurement because it eliminates, in advance, errors caused by misalignment of the composition of the points captured during measurement.
If you continue scanning a target for an extended period, errors will occur in the alignment of the points captured.
On the other hand, if you start scanning from a paused state, you can obtain a relatively accurate point cloud at the beginning of the scan.
Watch the video on how to scan.
The stop function is especially useful when used in the following measurement situations:
- The object needs to be measured as accurately as possible.
- The object needs to be measured by dividing it into multiple areas.
- You want to scan the area where you have missed collecting data.
- The object has a complicated geometry, such as curves.
- The object contains areas that need to be measured with extra care.
Photographic-style measurement
LiDAR scanner applications support one or both of the following measurement methods, depending on the application.
- Capturing points by moving the device after starting the measurement, as in video recording.
- Capturing points each time the shutter is pressed, as in photography.
Sakura3D SCAN supports both measurement methods.
One of the disadvantages of photographic-style measurement is that it is time-consuming, but it also has advantages, such as the resulting images contain less noise, and the user can control the device and measure only the required areas.
You can take measurements efficiently using different applications depending on the target object. For example, you can use the video-recording style measurement for objects with a simple geometry, such as planes, or the photographic-style measurement for objects with a complicated geometry or areas requiring extra care.
Watch the video on how to scan.
AI auto recognition feature
Sakura3D SCAN can distinguish between humans and non-humans using AI auto recognition.
Although not directly related to accuracy, this feature provides the following advantages when obtaining point clouds.
- Ease of measurement, as only the objects to be measured are identified and the number of unnecessary points is reduced.
- Because of the above advantages, post-processing becomes easy.
- There is no need for retakes if the image contains objects other than the target object.
Watch the video on how to scan.
Conclusion
Continuing from Part 1, this survey was conducted on the three subjects.
Considering the points mentioned in Part 1, our conclusions on 3D measurement using an iPhone/iPad LiDAR scanner are as follows:
- Distance to the target object: 0.3 to 5 m
- Well-lit location, whether indoors or outdoors
- Moderate point cloud density
- Do not expose a target object to the reflected light.
- An area up to 7 × 5 m in one shot
- Do not go back and forth too much.
- Make the most of the features of Sakura3D SCAN.
It has been found that useful data can be obtained by taking these points into consideration.
However, if the resulting point cloud is still unsatisfactory, you can easily retake the image. This is one of the advantages of the iPhone/iPad LiDAR scanner.
Feel free to try it.
How was it?
We hope this article helps you use LiDAR scanners.
We will continue to update this page with articles related to LiDAR scanners. Visit us again!
If you are interested in obtaining more information or have any questions, don‘t hesitate to contact us using the inquiry form.
tag : LiDAR Sakura3D SCAN
